Navigating India - The Journey of Ola Maps
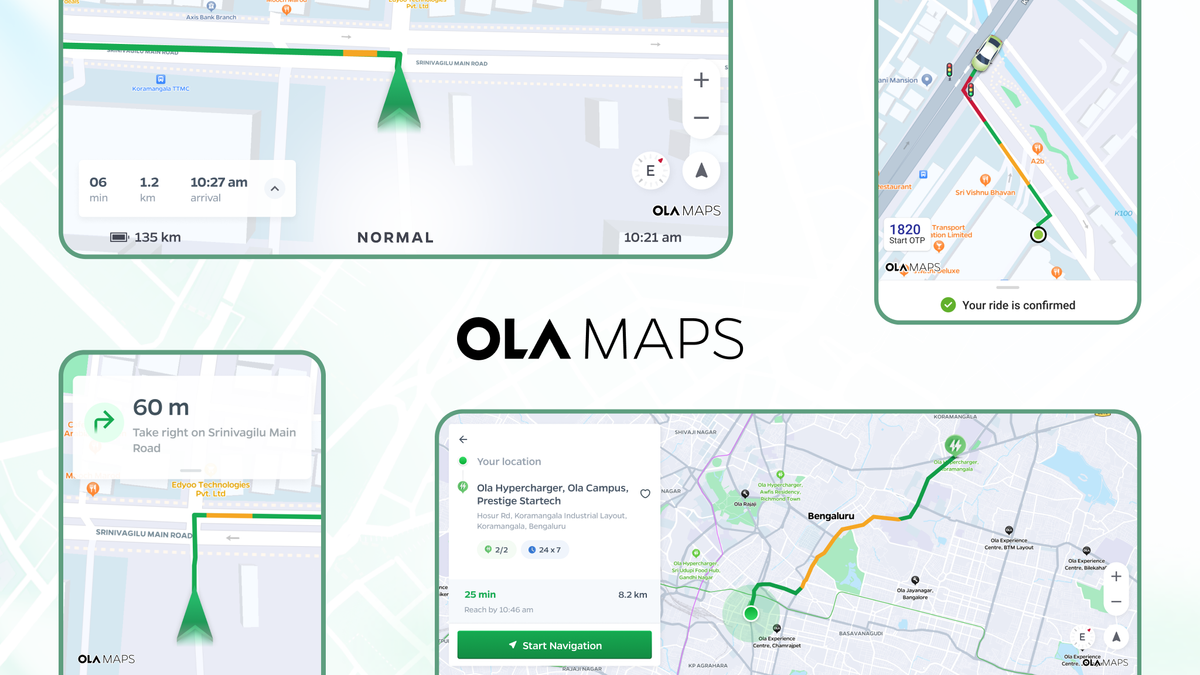
Mapping is a core pillar for mobility. They're not just about getting from point A to point B; they're about understanding the intricate web of streets, traffic patterns, and urban landscapes that define our cities. Humankind has always relied heavily on advancements in mapping technology, to progress in life.
In 2021, as the world started to move again in a post Covid era, we had plans to build first-to-world features on our customer and partner apps in Ola Mobility that would transform the user experience, but we quickly hit a roadblock. Our reliance on western mapping providers, for whom India wasn't a priority, severely limited our ability to implement these features. We realized that to truly serve our users and push the boundaries of mobility, we needed a true alternative to global mapping giants—one that was not only better suited for the Indian market but also more responsive to our unique needs. This realization sparked the inception of Ola Maps.
But why build our own maps when there are existing solutions?
The answer lies in our vision for the future of commerce and mobility. We're not just building maps for today: we're creating the cartographic infrastructure for tomorrow's mobility innovations. From autonomous vehicles to flying taxis to drones, the future of mobility demands maps that are more detailed, more dynamic, and more intelligent than ever before. We embarked on this ambitious journey three years ago, recognizing that to truly revolutionize mobility, we needed to own and innovate on every aspect of the maps experience that power our platform.
This post kicks off our 4-part series on Ola Maps. Here is what’s coming:
Part 1: The Foundation of Ola Maps (You are here)
Part 2: The Data Behind the Maps
Part 3: The AI Revolution in Mapping
Part 4: The Future of Maps
In the following sections of this blog, we'll dive deeper into the technology behind Ola Maps, the challenges we've overcome, and how this initiative is set to transform not just Ola, but the entire cartographic landscape. Stay tuned as we map out the future.
Section 1: Challenges & Opportunities while Building Maps for India
Existing mapping providers do not fully address unique challenges related to delivering a seamless experience for Indian users and this creates special opportunities for Ola and Indian developers.
Challenges
- Incomplete Mapping Coverage: Many streets and rural areas are not mapped or poorly mapped.
- Inconsistent and Varying Street Names: Street names often have variations and inconsistencies, leading to confusion.
- Frequent Changes in Road Networks: New streets are created, and existing ones are closed frequently, leading to outdated maps.
- Traffic and Road Condition Variability: Traffic patterns are highly inconsistent, and road conditions vary significantly due to potholes and non-standard streets.
- Non-Standardized Streets: Many streets do not conform to standard measurements and layouts.
- Potholes and Road Quality Issues: Potholes and road quality can significantly affect travel time and safety.
Opportunities
- Enhanced User Experience: Providing accurate and up-to-date maps can significantly enhance navigation and travel planning, improving user satisfaction.
- Localized Features: Offering features tailored to local needs, such as multi-language support, local business listings, and culturally relevant landmarks.
- Smart Navigation Systems: Developing smart navigation systems that can suggest optimal routes based on real-time data, considering traffic, road conditions, and user preferences.
- Integration with Smart City Initiatives: Collaborating with smart city projects to integrate mapping data with other urban infrastructure, enhancing overall city management and services.
- Augmented Reality Navigation: Utilizing AR to provide intuitive and immersive navigation experiences, especially in complex urban environments.
- Real-time Predictions: Using state of the art time series models to foresee traffic congestion, road closures, and other disruptions, offering proactive routing suggestions.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with local communities to crowdsource map updates and feedback, ensuring the map remains relevant and accurate.
- Eco-friendly Routing: Implementing eco-friendly routing options that minimize fuel consumption and emissions, appealing to environmentally conscious users.
- Real-time Data Updates: Implementing real-time data updates through IoT devices, GPS tracking, and user-reported changes can keep maps current.
- Local data residency: Ensure that critical data like location intelligence never leaves Indian soil
Addressing these unique challenges is not easy. In order to address them and tap the opportunities, we are leveraging three core resources: the power of AI, the power of open source and the power of the vast Indian talent ecosystem. This approach not only allows us to be more efficient but also ensures that our maps are built for delivering contextually relevant, accurate, safer and enhanced customer experience.
Section 2: Ola Maps Overview - Core Foundations
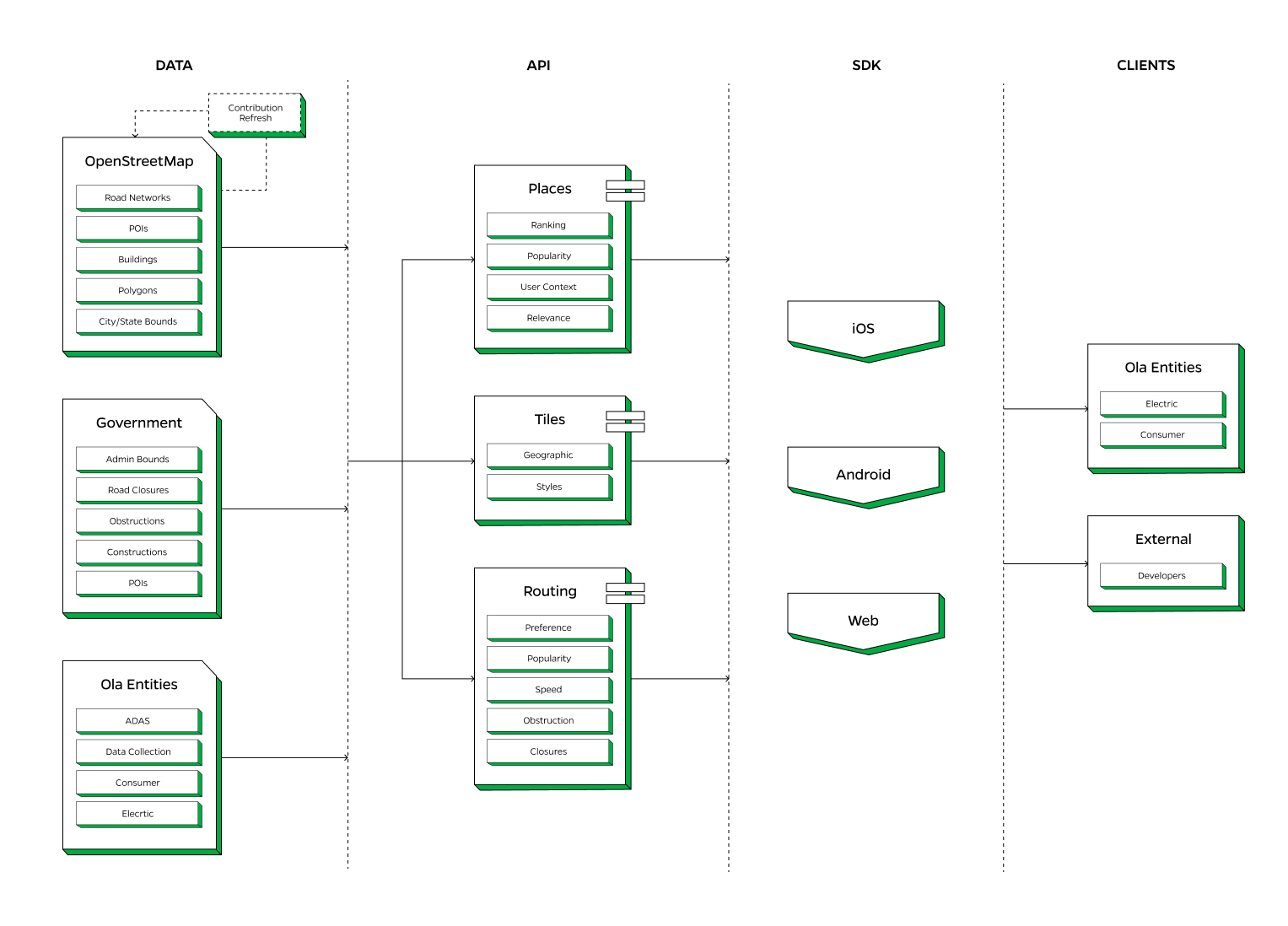
Ola Maps represents a sophisticated and integrated approach to digital mapping, combining multiple data sources, advanced AI algorithms, and user-friendly SDKs to deliver comprehensive navigation services. While the actual architecture is considerably more complex, we've distilled it down to its essential components to provide a clear, high-level understanding of the system's structure: Data, Places, Tiles, Routing and SDKs.
Data
For data sources, Ola Maps is built to utilize the most diverse set of data and send updates in near real time to ensure the most accurate mapping data as possible. Our AI first data systems utilize real time data from millions of vehicles using Ola Maps, fleet of Ola S1’s equipped with 360 cameras, open-source government data repositories, OpenStreetMap, partnerships and proprietary sources to build essential map features such as roads, points of interest, street furniture, building geometry and traffic signals. This highly comprehensive data system helps us with a robust mechanism for map expansion and map maintenance while allowing us to contribute to the open source community. In the past one year alone, we have contributed a total of 5.43 million edits to Open Street Maps.
Places
Ola Maps has adopted an AI-first approach to revolutionize our places system, responding to the generational shift in search and location-based services. We've integrated advanced machine learning and natural language processing to create a dynamic, context-aware places database. This system adapts in real-time to user needs and query intents, moving beyond static POI data to offer intelligent, predictive place information in multiple Indian languages.
Rendering & Tiles
Ola Map’s tiling system represents a strategic fusion of reliability and innovation. We've built upon an open-source rendering stack, leveraging its stability and community support for our base tiling needs. This gives us the strategic space to invest in cutting-edge NERF (Neural Radiance Fields) technology stack, pushing the boundaries of 3D scene reconstruction and view synthesis. This hybrid approach allows us to deliver consistent performance while gradually introducing photorealistic, dynamically rendered environments.
Routing
Ola Maps’ routing capabilities stand out due to their integration of preference-based routing, which tailors routes to user and vehicle preferences, and popularity-based routing, which suggests commonly used paths. Real-time and historical speed predictions provide accurate ETAs, while obstruction and closure management ensure routes are free from disruptions.
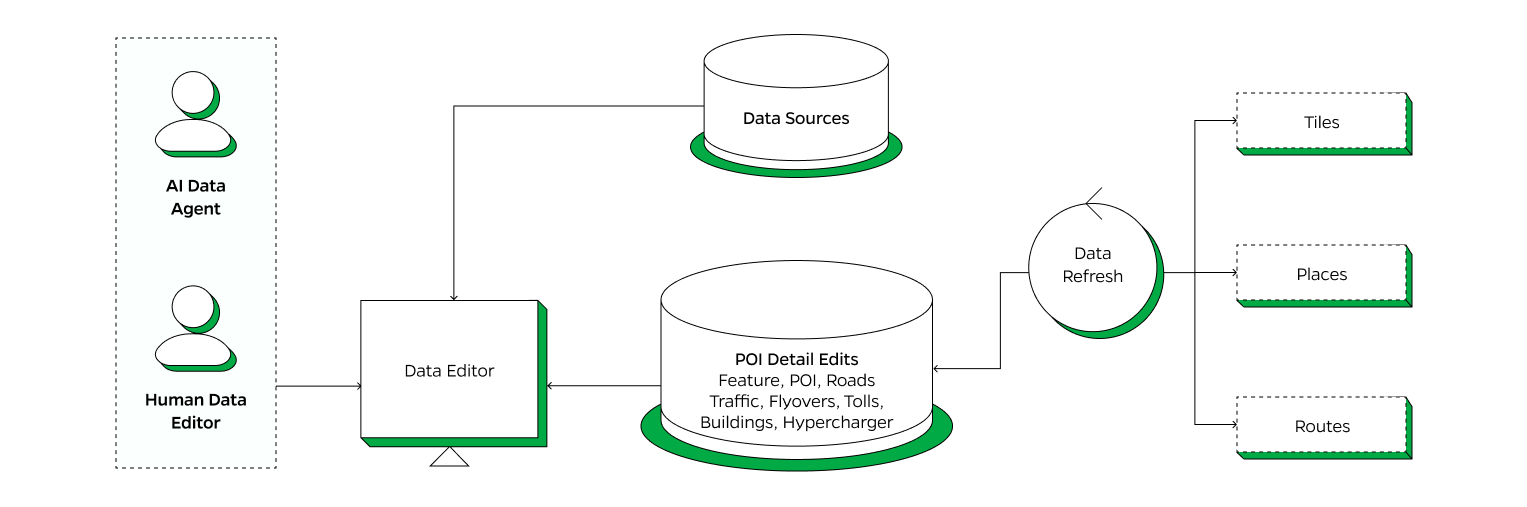
Ola Maps Data Ecosystem
This section gives a glimpse into our data ecosystem where we have different sources fed into our pipelines with AI agents augmented by a small number of highly skilled human data editors focusing on coding map features and updating our data layers.
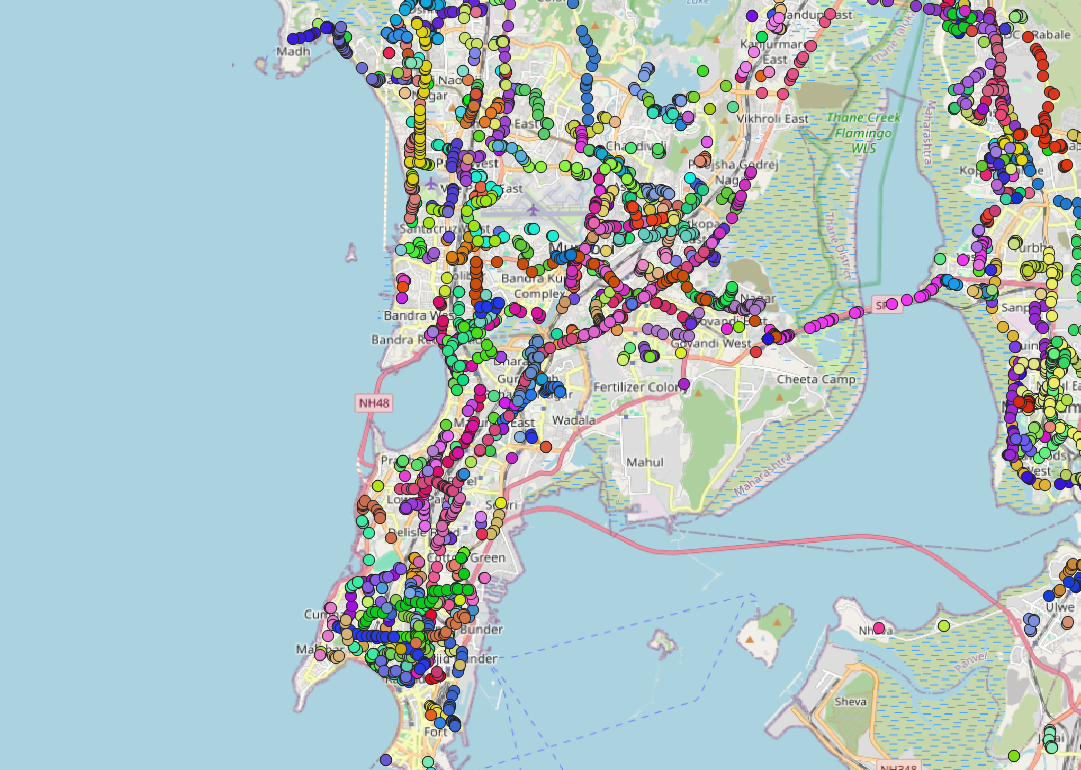
Data Sources
Our data ecosystem is built on the principle of crowd-sourced geo-mapping information leveraging Ola Maps massive user base, Open street maps, open source Government data repositories and other proprietary sources. Our system harnesses the wealth of location information generated by anonymised GPS pings & curated using AI models. The sensor data generated from 2-wheeler, 3-wheeler & 4-wheeler helps in identifying missing roads, real time traffic congestion & road restrictions and many such data points.
Data Platform
There is a highly sophisticated data platform in place which ingests more than 5 million messages per second from a multitude of sensors and telemetry sources. The data is centrally ingested, normalized, anonymized and then put in our Lakehouse hosting petabytes of data. Data streams coming from various sources are divided into further declarative pipelines to collect relevant data streams for training AI models, Analytics, and Data ops for Maps. The final output is put into Maps databases for Tiles, Places and Routes systems.
Data Editor Platform
The Data Editor Platform facilitates the integration, enhancement and continuous updating of mapping data. AI agents augmented by a small number of highly skilled human data editors focusing on coding map features and updating our data layers.
We will dive deeper into our Data Ecosystem and how we leverage Krutrim’s AI advanced capabilities in Part 2 & 3 of this blog series.
Ola Maps Places Platform
The Ola Maps Places Platform is a sophisticated system designed to handle a wide array of location-based services. The platform integrates various data sources, processes this data through advanced models, and ensures users receive accurate, relevant, and personalized location information, enhancing their overall navigation and search experiences.
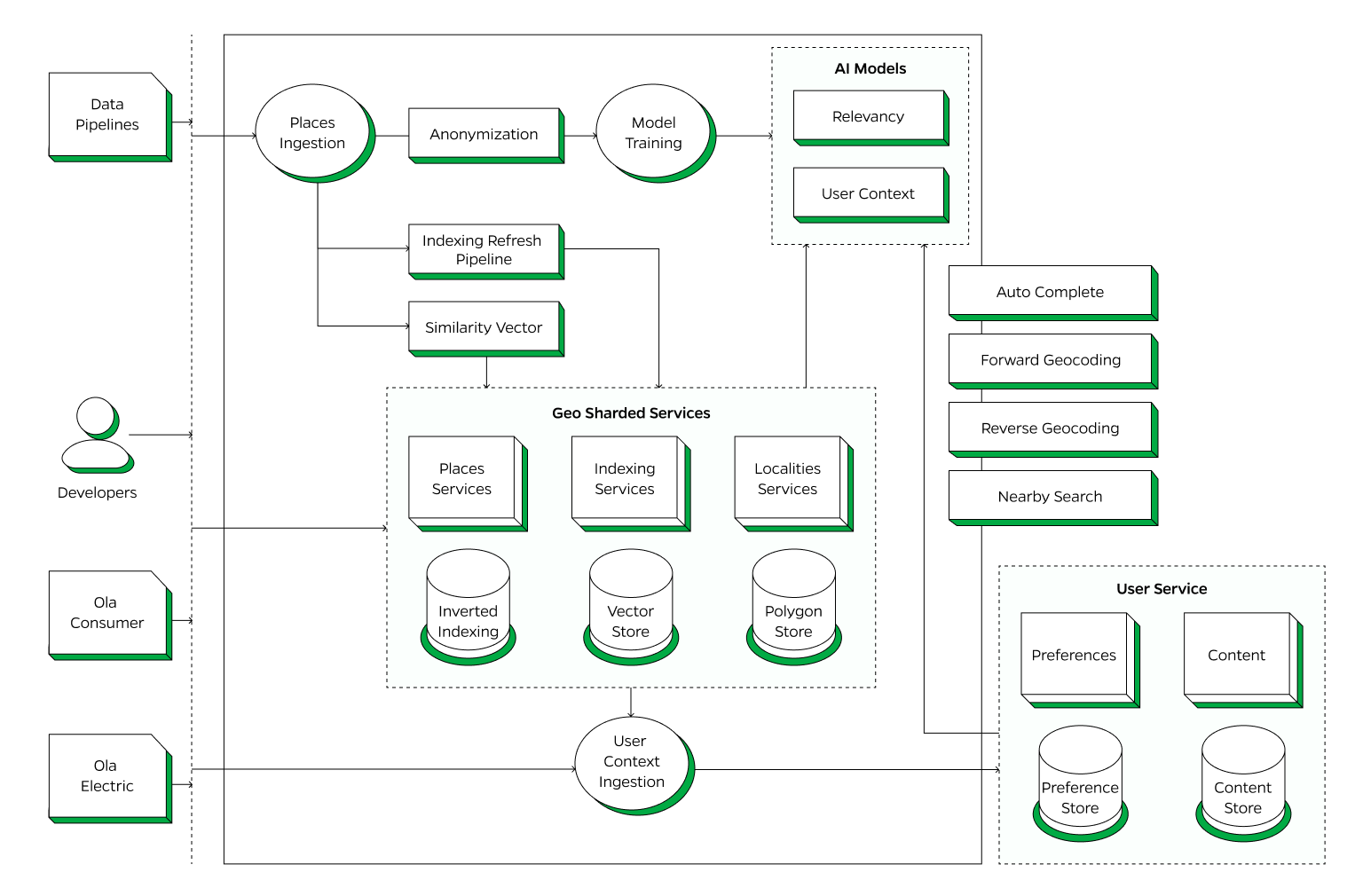
Data Ingestion and Anonymization
The process starts with data ingestion from various Data Pipelines. This raw data is funneled into the Places Ingestion component, where it undergoes initial processing. To protect user privacy, the data is anonymized, ensuring that no personally identifiable information is retained.
Indexing and Model Training
After anonymization, the data is fed into the Indexing Refresh Pipeline and processed to create Similarity Vectors. These vectors are essential for determining the relationships between different data points, improving the accuracy and relevance of search results. Simultaneously, the data is used for Model Training to develop advanced AI models focused on Relevancy and User Context. These models are crucial for enhancing the platform's ability to deliver precise and contextually appropriate search results.
Geo Sharded Services
The core of the platform is the Geo Sharded Services, which includes Places Services (manages detailed location information and Points of Interest), Indexing Services (utilizes Inverted Indexing and Vector Store to organize and store data efficiently, allowing for quick search and retrieval) and Localities Services (handles data related to specific localities, stored in the Polygon Store, which helps in defining and managing geographic boundaries).
User Context Ingestion
User interactions and contextual data are continuously ingested to refine the services further. This User Context Ingestion ensures that the platform can adapt to user behavior and preferences, delivering more personalized and relevant results.
User Service
User preferences are stored in the Preference Store, ensuring that the platform can deliver personalized experiences. Relevant content for users is managed and stored in the Content Store.
Autocomplete: The Autocomplete API dynamically enhances search functionality within various applications by identifying entities in user queries and suggesting relevant completions in real-time, significantly improving the user experience
Forward Geocoding: Geocoding API is a service that translates human-readable place names and addresses seamlessly into geographic coordinates, such as latitude and longitude.
Reverse Geocoding: Reverse Geocoding API is a robust tool crafted to effortlessly translate geographic coordinates into human-readable place names, spanning from precise street addresses to broader geographical areas
Nearby Search: Nearby Search API is a service that lets users find locations within a specified area.
Open Source usage in Places Platform
AI enablement of Places Platform
The Places platform leverages a host of custom-built advanced AI models to improve user experience.
POI Popularity and Classification
This model ranks and classifies Points of Interest (POIs) based on various factors like user interactions, frequency of visits, and user feedback. The classification helps in providing more relevant search results and recommendations to users.
Search Relevancy Ranking
This model ensures that the most relevant POIs appear at the top of the search results by using state of the art mBERT (multilingual encoder) based Named Entity Recognition (NER), Learning to Rank (LTR) models and natural language processing (NLP) techniques. The model takes into account factors like query context, user preferences, and historical search data to rank the results effectively.
Contextual Search Identification
This model understands and processes context-based search queries to provide accurate results. This is done by syntactic and semantic search models like Bi-LSTM-CRF. It also leverages NLP and contextual analysis to comprehend the intent behind user searches. This model uses contextual cues and user behavior patterns to fine-tune search results.
We will dive deeper into how AI has enabled us to build a world class mapping platform at a fraction of time & cost in Part 3 of this blog series “The AI Revolution in Mapping”.
Ola Maps Routing Platform
The Ola Maps Routing Platform is designed to deliver precise and efficient navigation services through a sophisticated data processing and routing system. The platform integrates data from various sources, including real-time signals, to generate accurate direction’s and ETA’s.
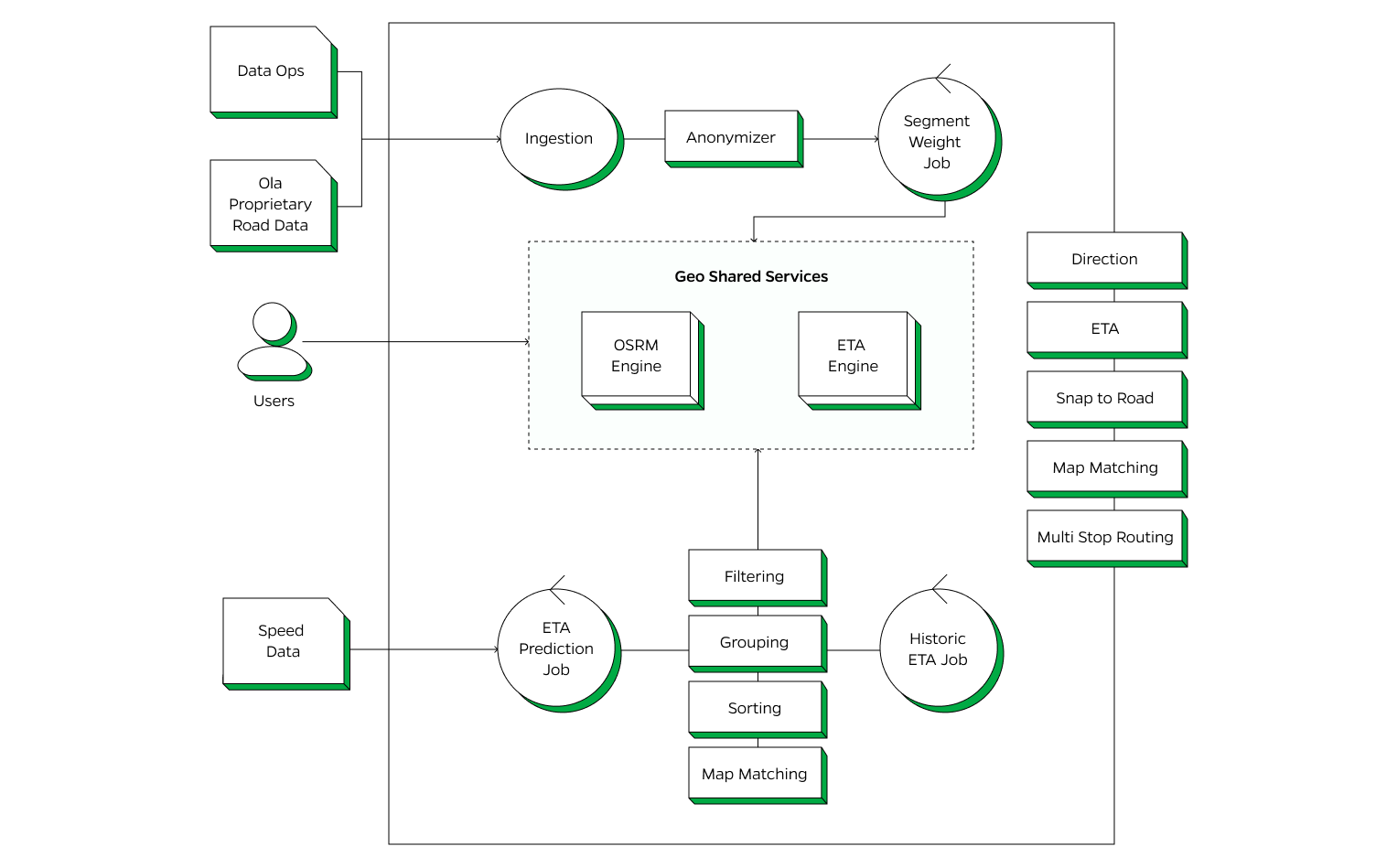
Users interact with the routing platform, and their inputs are processed through the geo-sharded services to deliver efficient routing solutions. The platform supports multiple advanced routing features:
Directions: Provides turn-by-turn navigation instructions to guide users from their starting point to their destination.
ETA: Calculates the Estimated Time of Arrival based on current and historical traffic data to provide accurate travel times.
Snap to Road: Aligns user-reported positions to the nearest road, correcting any GPS inaccuracies to reflect real-world driving paths.
Map Matching: Ensures that GPS traces are accurately aligned with the road network by matching them to the correct paths on the map.
Multi Stop Routing: Enables planning and navigating routes with multiple destinations, optimizing the order of stops for efficiency.
Open Source usage in Routing Platform
AI enablement of Routing
We have built models to enhance our Routing service offering while improving user experience.
Vehicle Pings Analysis: Uses real time data streams from multiple sources to predict road segment speeds, identify roads, traffic conditions and potential disruptions. It helps in dynamically adjusting routes based on current road conditions and traffic flow.
Road Closure Model: Identifies temporary and permanent road closures to enhance routing accuracy by utilizing real time data from government sources, social media and vehicle pings to detect road closures. The model continuously updates the routing engine to avoid closed roads and suggest alternative routes.
Speed Prediction: Leverages neural network based time series models using historical data to estimate travel times more accurately where realtime coverage is less.
Road Popularity Model: Aggregates data from various sources, including vehicle pings, user preferences and user feedback, road classifications to assess the popularity of different roads. Popular routes are prioritized for routing suggestions, ensuring that commonly used and trusted paths are recommended to users.
Ola Maps Tiles Platform
The Ola Maps Tiles Service is a key component designed to generate and serve map tiles, ensuring that users have access to detailed and visually appealing maps.
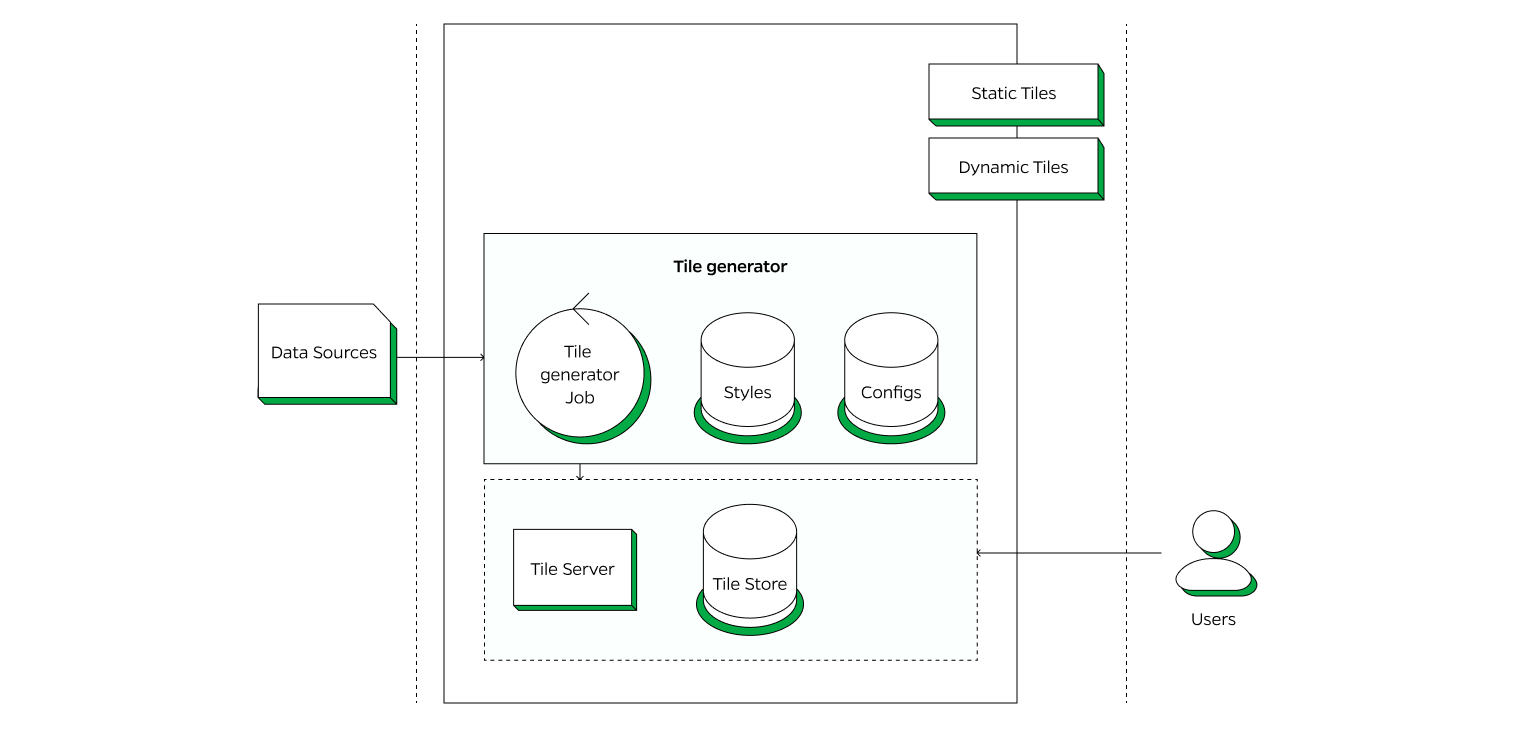
Tile Generator
The Tile Generator is responsible for processing the ingested data to create map tiles. It leverages the configurations that define the visual appearance, such as colors, line styles, and icons as well the settings that determine how the tiles are generated and displayed, ensuring consistency and usability across different platforms and devices.
Tileserver
Tileserver creates a map instance on the server-side (leverages the Open Source Maplibre library) with local styles, fonts, sprites and tilesets. This setup is used for rendering the base map of static map tiles. A transparent image with markers, polylines and watermark is overlaid on the base map image to produce the final map output.
Open Source usage in Tiles Platform
Section 3:. Impact on Customer Experience
Ola Maps has been going live across the Ola ecosystem and our users are loving it.
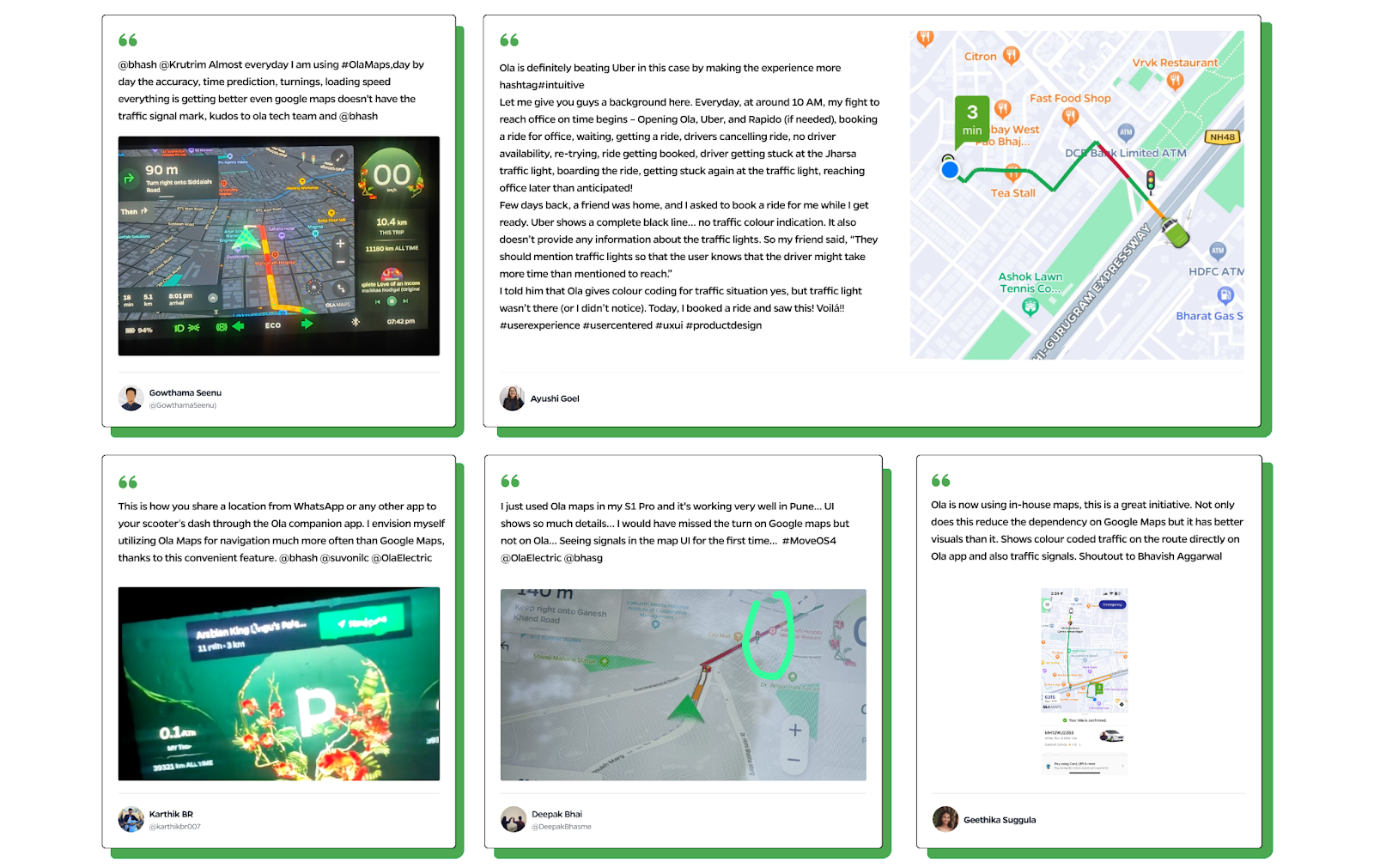
Ola Maps in Ola Electric Ecosystem
Every day tens of thousands of customers use Ola Maps on their scooters and the Ola Electric app for a guided commute to places in their cities. The platform serves over a million search queries everyday for Ola Electric users. Use of on-device navigation has gone up 4x since the launch of Ola Maps in MoveOS 4 and in a recent survey, it was voted as the top feature in MoveOS4.
Ola Maps in Ola Consumer Ecosystem
Ola Maps forms the core of our Ola Consumer platform: it forms the base layer of our apps, helps match the rider - driver pair, provides key inputs to our price prediction algorithms, powers all the pick up and drop off experiences and the core navigation experience for all our driver & delivery partners. Our enhanced places platform now outperforms our previous map provider both in terms of accuracy (due to superior user context) and latency. Users love the detailed information about their cab’s route to their location with detailed traffic states and traffic lights powered by the Ola Maps tile platform. The routing engine has significantly improved our pricing prediction and allocation algorithms leading to 2% lesser pricing deviations, 9% lesser cancellations and 6% more accurate pickups.
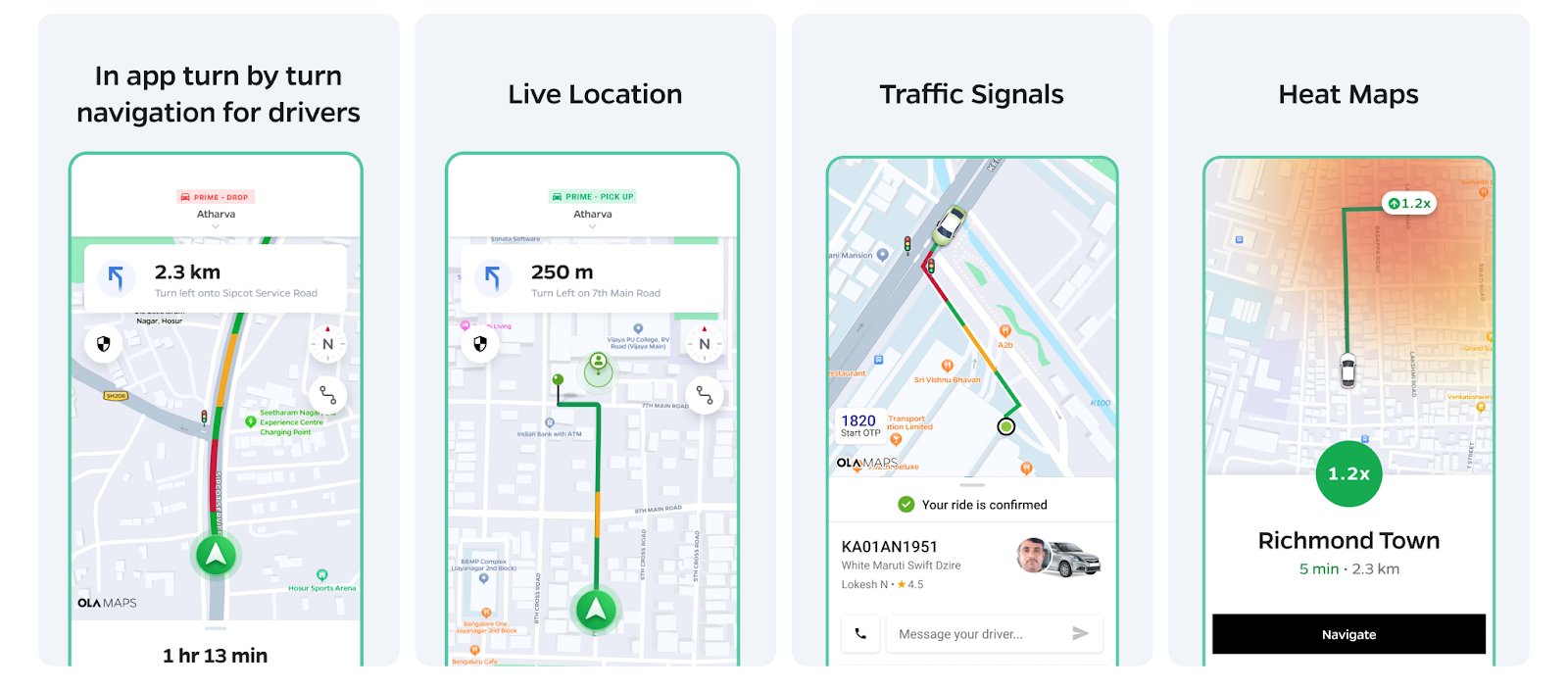
Comparison of key performance metrics
The Ola Maps platform today outperforms our previous map providers on key performance metrics for the Ola users.
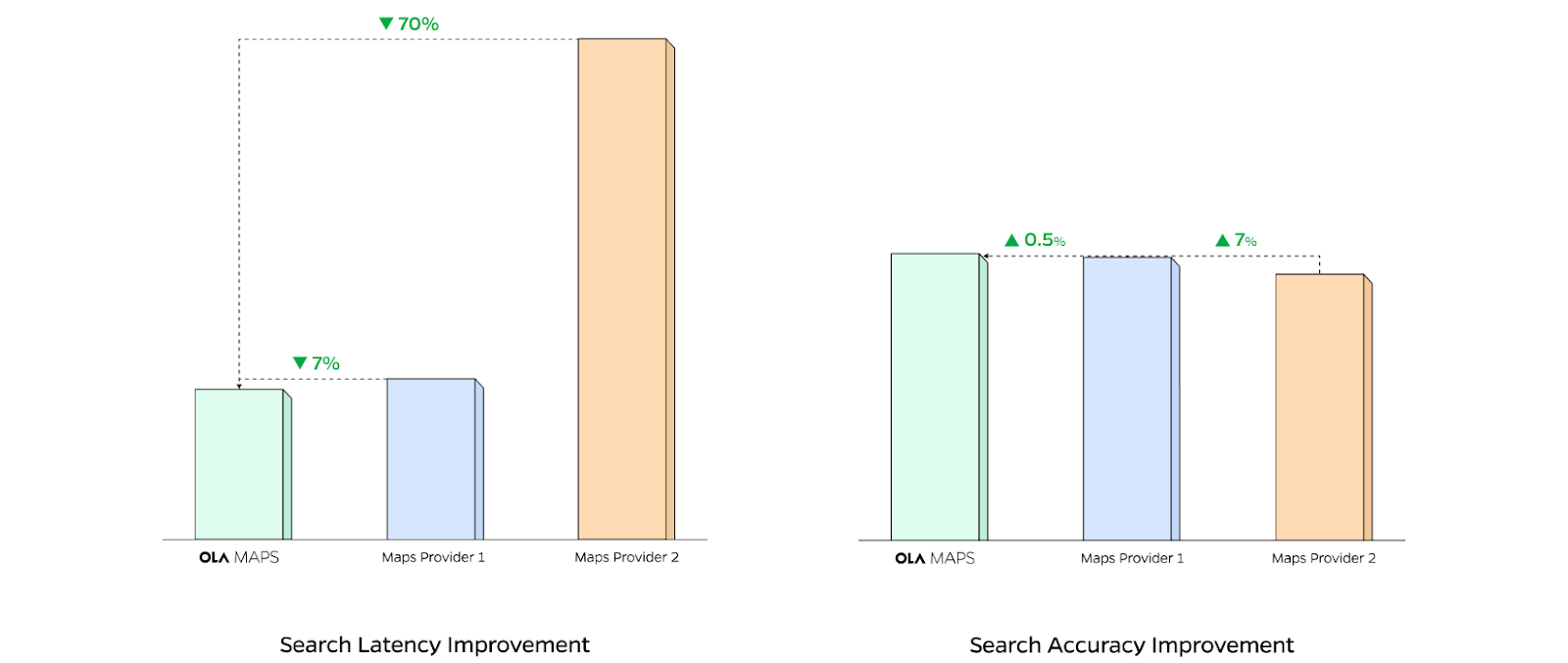
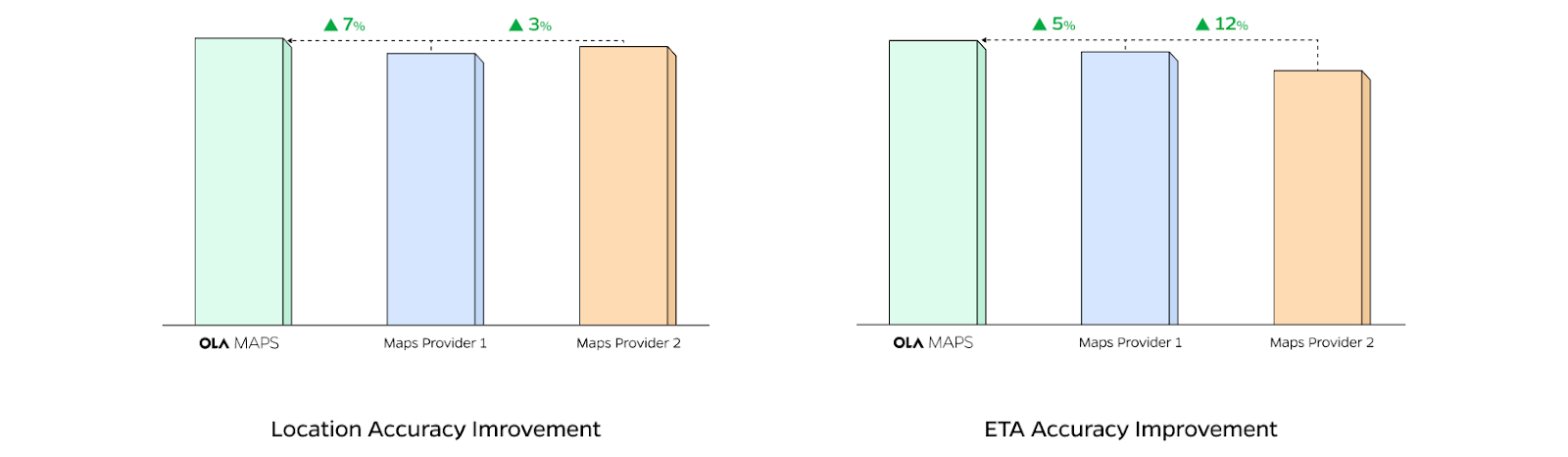
Impact on external map providers
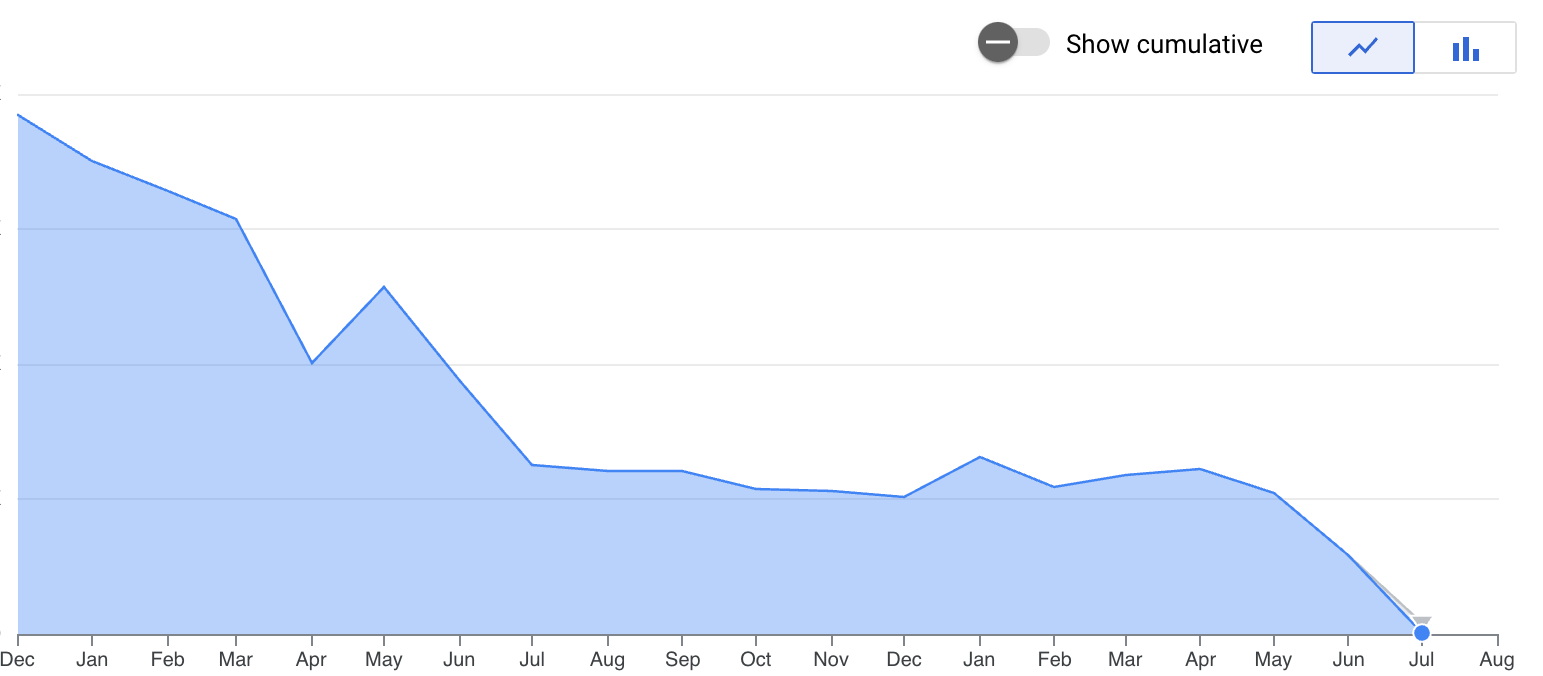
Over multiple launches, AB experiments and product iterations, the Ola Maps platform has outperformed our external map providers across all services, geographies and form factors. With every release, our reliance on external map providers has come down. And in the month of July, it is going to be ZERO! This has allowed us to invest our resources into building significantly better experiences for our customers and to imagine the future of mapping!
We hope that you enjoyed reading about our journey of building Ola Maps and the core foundations of the system. Stay tuned for our deep dive into the world of Ola Maps in our upcoming installments where we'll explore the intricate data foundations, cutting-edge AI applications, and our vision for the future of mapping technology. Don't miss these insights into how we're reshaping the landscape of location-based services.
- Team Ola Maps

